Shopping List Generator
Meal prep made easy. Simplify the most difficult part of your weekly shop– the planning!
This web app simplifies the daunting task of meal prepping by generating a comprehensive shopping list based on your chosen meals. Simply build your favourite meals by listing their ingredients and their quantities, then common ingredients are combined into a single shopping list for you, with the ability to tick items off as you go.
MySQL
First of all, we define the database:
- Meals: Lists meals with names and descriptions.
- Ingredients: Stores ingredients, to be used within the context of a meal or shopping list item.
- Meal Ingredients Link: Connects meals to their ingredients, with quantities and units.
- Shopping Lists: Holds shopping lists, linked to a specific user.
- Shopping List Items: Contains items on shopping lists, linked to specific ingredients with quantities.
- Users: Stores user details.
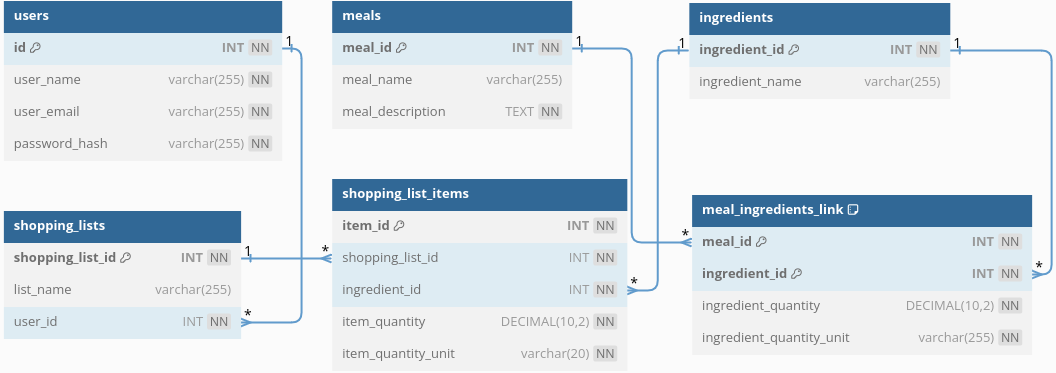
Ingredients are the base unit for the entire applications function. Meals are mapped to these through an intermediate table, tracking quantities and the units of these quantities (grams, millilitres, etc.).
REST API (Spring Boot)
My Spring Boot API uses JDK 17, Spring Data JPA, and MySQL connector J to connect to my database and persist objects from it.
I've taken a standard Spring approach to effectively model my database, providing an Entity, Controller and Repository for each database table. Many of these entities are defined exactly according to my database definition, using the JsonIgnore annotation where appropriate to avoid cyclical references. Relationships between these entities are also modelled through joins, such as:
@Entity
@Table(name = "meals")
public class Meal {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "meal_id")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "meal_name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "meal_description", columnDefinition = "TEXT", nullable = false)
private String description;
@ManyToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinTable(
name = "meal_ingredients_link",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "meal_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "ingredient_id")
)
private Set ingredients;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "meal", cascade = CascadeType.ALL, orphanRemoval = true)
private Set mealIngredients = new HashSet<>();Some additional classes had to be created, such as to model the composite key for the meal-ingredient link table:
@Embeddable
public class MealIngredientId implements Serializable {
@Column(name = "meal_id")
private Long mealId;
@Column(name = "ingredient_id")
private Long ingredientId;
Within my ShoppingList Entity class, I've defined this method, combineItems(), to provide the main
application functionalitity by intelligently consolidating individual shopping list items into grouped quantities.
Shopping list items are bundled together and their combined quantities are
saved to the list's `items` field. It's defined in an object-oriented way, where a shopping list
is responsible for its own items ArrayList.
This method is called whenever a shopping list is returned,
so that the user always receives an aggregated list.
To summarise this method:
- A HashMap is created.
- Each existing shoppingList item is iterated and a composite key of the ingredient's id value and quantity unit is created then added to a hashmap as a key, mapped against the quantity amount.
- If one of these composite keys already exist in the HashMap, the existing quantity amount is added to that of the current ingredient quantity in the HashMap.
- Once all items have been iterated, we know that our list has been combined. At this point, we overwrite our old, un-aggregated items field with our newly combined one.
public void combineItems() {
// HashMap map items by ingredientId and quantityUnit against ShoppingListItem
HashMap groupedItems = new HashMap<>();
// Iterate all current ShoppingListItems
for (ShoppingListItem item : items) {
// Create a composite HashMap key made up of current list item's id and quantity unit
String key = item.getIngredient().getIngredientId() + "_" + item.getItemQuantityUnit();
// If current item exists with same quantity unit
if (groupedItems.containsKey(key)) {
// Get existing item
ShoppingListItem existingItem = groupedItems.get(key);
// Sum the quantity of current item with the existent one
BigDecimal combinedQuantity = existingItem.getItemQuantity().add(item.getItemQuantity());
// Update existent quantity with sum
existingItem.setItemQuantity(combinedQuantity);
} else {
// Item doesn't exist in the map, add it to it
groupedItems.put(key, item);
}
}
// Update items list with the combined items
items = new ArrayList<>(groupedItems.values());
}Within my controller, I've defined a number of useful API end points. Here is the main one, where a list of user-supplied JSON ingredients are used to create a new, aggregated shopping list:
@PostMapping("/create/{listName}")
public ResponseEntity createShoppingListFromIngredients(
@PathVariable String listName,
@RequestBody List shoppingListItems) {
// Create a new ShoppingList and set its name
ShoppingList shoppingList = new ShoppingList();
shoppingList.setListName(listName);
// Save the shopping list to the database using the repository
ShoppingList savedShoppingList = shoppingListRepository.save(shoppingList);
// Iterate and associate ShoppingListItems with the new ShoppingList
for (ShoppingListItem item : shoppingListItems) {
item.setShoppingList(savedShoppingList);
}
// Save the updated ShoppingListItem objects
List savedItems = shoppingListItemRepository.saveAll(shoppingListItems);
// Set the list of saved ShoppingListItem objects back to the ShoppingList
savedShoppingList.setItems(savedItems);
// Combine the items using the combineItems method
savedShoppingList.combineItems();
return ResponseEntity.ok(savedShoppingList);
}JSON Request/Reponse
An example of a structured JSON request to this method, with API endpoint `lists/create/New List`, might be:
[
{
"ingredient": {
"ingredientId": 2,
"ingredientName": "Bell Peppers"
},
"itemQuantity": 2.00,
"itemQuantityUnit": "pieces"
},
{
"ingredient": {
"ingredientId": 2,
"ingredientName": "Bell Peppers"
},
"itemQuantity": 4.00,
"itemQuantityUnit": "pieces"
},
{
"ingredient": {
"ingredientId": 1,
"ingredientName": "Chicken Breast"
},
"itemQuantity": 300.00,
"itemQuantityUnit": "grams"
}, {
"ingredient": {
"ingredientId": 1,
"ingredientName": "Chicken Breast"
},
"itemQuantity": 300.00,
"itemQuantityUnit": "grams"
}
]Which would return:
{
"shoppingListId": 5,
"listName": "New List",
"items": [
{
"itemId": 21,
"ingredient": {
"ingredientId": 1,
"ingredientName": "Chicken Breast"
},
"itemQuantity": 600.00,
"itemQuantityUnit": "grams"
},
{
"itemId": 19,
"ingredient": {
"ingredientId": 2,
"ingredientName": "Bell Peppers"
},
"itemQuantity": 6.00,
"itemQuantityUnit": "pieces"
}
]
}As you can see, the structured JSON gives a combined list of user-supplied ingrdients (in this example, 2x 300g Chicken Breast becomes 600g Chicken Breast and 2+4 pieces of Bell Peppers becomes 6 pieces). Firstly, supplied ingredients (with their quantities and units) are saved to the database as shopping list items. Then, a shopping list is saved, with the new list items added in. The last part of the request path is also used to set the list name. A list id is returned also, to allow this list to be retrieved again and edited on the client-side, then re-saved.
User Journey
The app begins by displaying an empty meal list. Users can add meals by clicking a button that opens a modal with a search box. They can either select an existing meal or create a new one. Meals consist of a name, description, and a list of ingredients with quantities and units.
When an existing meal is selected, its details populate the modal for editing before being added to the list. If creating a new meal, the modal starts blank. Users can add ingredients dynamically and save the meal.
The meal list allows users to add, edit or delete meals. Once the desired meals are selected, the user generates their shopping list. This aggregated list combines ingredients from all meals, showing totals for each item. Ingredients have checkboxes to mark them as purchased, moving them to a separate list of inactive items at the bottom of the screen.
Users can also add custom, non-meal-related items to the shopping list. At any point, they can return to the meal list to add or modify meals and update the shopping list.
React UI
All of the app's components are conditionally rendered based on the managed states which are toggled. There are two main screens, MealList & ShoppingList. Within App.js, these are conditionally rendered, based on the current context of the app's usage (where showMealList is set). The MealList is displayed by default.
The app consists of two main components: MealList and ShoppingList. These are conditionally rendered based on the app's state.
MealList Component: Displays meals retrieved from the database via an API call. Meals are dynamically rendered as list items. Users can edit, delete, or adjust meal quantities using buttons. New meals can be created or existing ones modified using a modal with input fields for meal details and ingredients.
<ul className="meal-list">
{userSelectedMeals.map((meal) => (
<li key={meal.id} className="meal-item">
<div className="meal-actions">
<Button
icon
className="edit-button"
onClick={() => incrementMealQuantity(meal)}
>
<Icon name="plus" />
</Button>
<Button
icon
className="edit-button"
onClick={() => decrementMealQuantity(meal)}
>
<Icon name="minus" />
</Button>
</div>
<div>
<h3>{meal.mealQuantity || 1}</h3>{" "}
{/* Display mealQuantity, if it exists. If not, show 1. */}
</div>
<div className="meal-details">
<div>
<h3>{meal.name}</h3>
<p>{meal.description}</p>
</div>
</div>
<div className="meal-actions">
<Button icon className="edit-button" onClick={() => editMeal(meal)}>
<Icon name="pencil" />
</Button>
<Button
icon
className="delete-button"
onClick={() => handleDeleteMeal(meal.id)}
>
<Icon name="trash" />
</Button>
</div>
</li>
))}
</ul>ShoppingList Component: Aggregates ingredients from the selected meals. Items are displayed with checkboxes for marking them as purchased, which moves them to an inactive list. Users can also add custom items via a modal.
<Modal>
<Modal.Header>
<div style={{ textAlign: "center" }}>
<Header>Add Meal</Header>
</div>
<Label className="meal-details-label">Meal Name:</Label>
<Input
className="meal-details-input"
value={mealName}
onChange={(e) => setMealName(e.target.value)}
/>
<Label className="meal-details-label">Meal Description:</Label>
<Input
className="meal-details-input"
value={mealDescription}
onChange={(e) => setMealDescription(e.target.value)}
/>
</Modal.Header>
<Modal.Content>
<Modal.Description>
<Header>Ingredients</Header>
<List divided relaxed>
{ingredients.map((ingredient, index) => (
<IngredientItem
key={index}
ingredient={ingredient}
onRemove={(ingredientToRemove) => {
const updatedIngredients = ingredients.filter(
(ing) => ing !== ingredientToRemove
);
setIngredients(updatedIngredients);
}}
/>
))}
</List>
<div className="ingredient-adder">
<Label className="ingredient-details-label">Ingredient Name:</Label>
<Input
placeholder="Enter ingredient name..."
value={selectedIngredient}
onChange={(e) => setSelectedIngredient(e.target.value)}
/>
<Label className="ingredient-details-label">Quantity:</Label>
<Input
type="number"
min="1"
value={quantity}
onChange={(e) => setQuantity(e.target.value)}
/>
<Label className="ingredient-details-label">Quantity Unit:</Label>
<Dropdown
placeholder="Select unit..."
fluid
selection
options={quantityUnitOptions.map((unit) => ({
key: unit,
text: unit,
value: unit,
}))}
value={quantityUnit}
onChange={(e, { value }) => setQuantityUnit(value)}
/>
<div className="control-buttons">
<Button color="green" onClick={addIngredient}>
<Icon name="plus" /> Add Ingredient
</Button>
<Button color="teal" onClick={handleSaveMealClick}>
<Icon name="check" /> Save meal to list
</Button>
{showErrorLabel && (
<Label color="red" pointing="above" className="error-label">
Please add a meal name, description and ingredients before saving.
</Label>
)}
<Button color="red" onClick={onClose}>
<Icon name="remove" /> Cancel
</Button>
</div>
</div>
</Modal.Description>
</Modal.Content>
</Modal>The shopping list dynamically displays aggregated ingredients and their quantities from selected meals. Users can mark items as purchased, which moves them to an inactive list displayed below. This helps track shopping progress in real-time.
<div className="shopping-list-container">
<h1>Shopping List</h1>
<p>id: {shoppingList.shoppingListId}</p>
<List divided relaxed className="shopping-list">
{shoppingList.items.map((item, index) => (
<ShoppingListItem
key={index}
item={item}
onRemove={() => removeItem(item)}
onToggle={() => toggleItem(item)}
inactiveItems={inactiveItems}
/>
))}
</List>
{/* Render the inactiveItems list similarly */}
<List divided relaxed className="shopping-list-inactive">
{inactiveItems.items.map((item, index) => (
<ShoppingListItem
key={index}
item={item}
onRemove={() => removeItem(item)}
onToggle={() => toggleItem(item)}
inactiveItems={inactiveItems}
/>
))}
</List>
<NewListItem shoppingList={shoppingList} setShoppingList={setShoppingList} />
<Button className="add-button shopping-button" onClick={toggleShowMealList}>
Go back to Meals
</Button>
</div>API Calls
API calls use the asynchronous fetch() API to communicate with the backend. Meals and shopping lists are retrieved, updated, or created by sending structured JSON data.
useEffect(() => {
// Fetch meals from API
fetch('https://grocery.alexs-apis.xyz/meals/allmeals')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => setMeals(data))
.catch((error) => console.error('Error fetching meals:', error));
}, [modalOpen]);API Calls
For example, when generating a shopping list, the app sends meals, structured as ingredient quantities to the backend. Ingredients are then aggregated and quantitiy units are converted meal quantities. The backend then returns the updated or newly created shopping list.
const generateShoppingList = async () => {
console.log("Shopping List ID:", shoppingList.shoppingListId);
console.log("List: ", shoppingList);
if (userSelectedMeals.length > 0) {
if (shoppingList.shoppingListId != null) {
// Updating an existing list
const requestBody = userSelectedMeals.flatMap((meal) =>
meal.ingredients.map((ingredient) => ({
ingredient: {
ingredientId: ingredient.ingredientId,
ingredientName: ingredient.ingredientName,
},
itemQuantity: ingredient.quantity * (meal.mealQuantity || 1), // multiply the ingredient amount by how many entries of that meal there are, or 1, if no copies
itemQuantityUnit: ingredient.quantityUnit,
}))
);
console.log("Updating shopping list with: ", requestBody);
try {
const response = await fetch(
`https://grocery.alexs-apis.xyz/lists/update/${shoppingList.shoppingListId}`,
{
method: "PUT",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(requestBody),
}
);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
const responseData = await response.json();
console.log("Shopping list updated:", responseData);
// Update shopping list in the master container
setShoppingList(responseData);
toggleShowMealList();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error updating shopping list:", error);
}
} else {
// Creating a new list
let requestBody = userSelectedMeals.flatMap((meal) =>
meal.ingredients.map((ingredient) => ({
ingredient: {
ingredientId: ingredient.ingredientId,
ingredientName: ingredient.ingredientName,
},
itemQuantity: ingredient.quantity * (meal.mealQuantity || 1), // multiply the ingredient amount by how many entries of that meal there are, or 1, if no copies
itemQuantityUnit: ingredient.quantityUnit,
}))
);
console.log("Creating shopping list with: ", requestBody);
try {
const response = await fetch(
"https://grocery.alexs-apis.xyz/lists/create",
{
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify(requestBody),
}
);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
}
const responseData = await response.json();
console.log("Shopping list created:", responseData);
// Update shopping list in the master container
setShoppingList(responseData);
toggleShowMealList();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error creating shopping list:", error);
}
}
} else {
// If saving a meal without the required fields filled
setShowErrorLabel(true); // Show the error label
setTimeout(() => {
setShowErrorLabel(false); // Hide the error label after 2.5 seconds
}, 2500);
console.error("Add meals before trying to generate a list");
}
};
